Quality assurance (QA) testing isn’t a final step; it’s an engine for reliability, compliance, and user trust. In 2025, businesses run continuous delivery pipelines where speed without quality equals risk.
This guide covers every type of QA testing, community-backed best practices, and insights from real Reddit threads that show what QA engineers actually face in the field.
1. Why QA Testing Matters in 2025
Software moves faster than ever — CI/CD, microservices, AI releases — and every deployment can impact customers instantly. QA keeps that speed safe.
“Our team is dealing with an increasing number of flaky UI test failures, and it’s honestly draining the team’s time in our automation suite.”
Flaky automation, rushed builds, or poor test coverage don’t just break code — they break user trust, delay releases, and drain developer morale.
2. The QA Testing Ecosystem
2.1 Planning and Strategy
Start by defining risk appetite, SLAs, and quality goals. Align QA metrics with business outcomes like uptime, conversion, and NPS.
2.2 Environment Setup
Mirror production. Mismatched environments cause most false failures.
“Unstable environments constantly lead to test flakiness. Screenshot-based testing which requires baseline updates…”
2.3 Execution and Monitoring
Use real-time dashboards. Pattern detection in defect data saves time — don’t just fix bugs, fix where they originate.
2.4 Continuous Feedback
Treat QA as a feedback system, not a gate. Post-release analytics, root-cause analysis, and test refactoring keep quality improving.
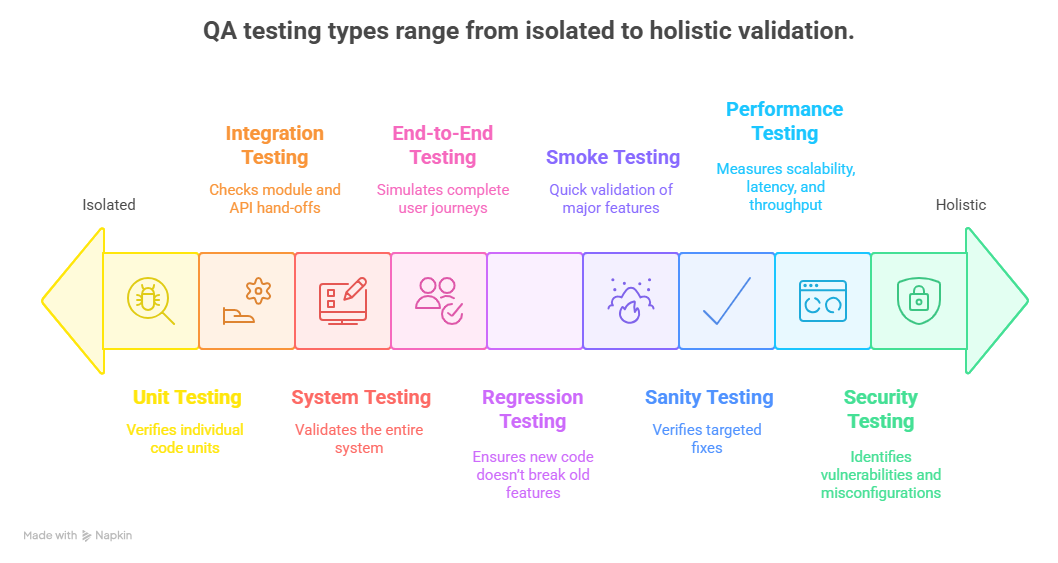
3. The 12 Core Types of QA Testing
| # | Testing Type | Purpose | When to Apply |
| 1 | Unit Testing | Verifies individual code units or functions. | Continuous integration; early bug prevention. |
| 2 | Integration Testing | Checks module and API hand-offs. | After unit tests; before staging. |
| 3 | System Testing | Validates the entire system meets requirements. | Before release. |
| 4 | End-to-End (E2E) | Simulates complete user journeys. | Critical revenue or compliance flows. |
| 5 | Regression Testing | Ensures new code doesn’t break old features. | After every build. |
| 6 | Smoke Testing | Quick validation that major features run. | Immediately after deployment. |
| 7 | Sanity Testing | Verifies targeted fixes before full regression. | Post-hotfix cycles. |
| 8 | Performance / Load | Measures scalability, latency, and throughput. | Peak seasons or major launches. |
| 9 | Security / Penetration | Identifies vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. | Always; before exposing to users. |
| 10 | User-Acceptance (UAT) | Confirms the software meets business needs. | Before go-live. |
| 11 | Accessibility (WCAG 2.2) | Ensures inclusivity and compliance. | All public-facing releases. |
| 12 | AI-Driven / Self-Healing | Uses ML to predict failures, auto-repair scripts. | Mature QA pipelines with CI analytics. |
4. Choosing the Right Mix
The goal isn’t to run every test — it’s to choose what gives the most confidence per dollar.
- Focus E2E on “money paths.”
- Keep 70 % of automation at unit level; 20 % integration; 10 % E2E.
- Invest in non-functional tests — performance and security issues destroy reputation faster than functional bugs.
5. Common Pitfalls and Fixes
| Pitfall | Impact | Fix |
| Over-automation | Brittle suites, slow feedback | Start small, automate regression only |
| Environment drift | False negatives | Containerize and match production configs |
| Ignoring non-functional tests | Hidden risk | Integrate performance and security in CI |
| Flaky UI tests | Eroded trust in automation | Stabilize data, fix waits, prune bad tests |
| No clear QA metrics | Invisible ROI | Track MTTD, MTTR, escaped defects |
6. Practitioner Insights (Reddit & QA Forums)
“E2E brings confidence but is costly and fragile; keep it to golden paths.”
“Manual testers still catch things automation can’t—especially flows with emotion or context.” — r/softwaretesting
“Testing imo is perennial … automation is expensive and catches fewer UX bugs.” — r/softwaretesting
These comments echo a universal truth: automation is a force multiplier, not a replacement for human insight.
7. 90-Day Implementation Plan
Days 1–30:
- Audit current test suites and flake rates.
- Stabilize CI/CD environments.
- Add smoke and API contract tests.
Days 31–60:
- Enforce developer-owned unit tests for critical code.
- Introduce performance and security gates.
Days 61–90:
- Add mutation testing for coverage quality.
- Publish a QA dashboard for leadership visibility.
QA Testing FAQs
1. What are the main types of QA testing?
Twelve core types exist: unit, integration, system, end-to-end, regression, smoke, sanity, performance, security, user-acceptance, accessibility, and AI-driven testing.
2. How is QA different from software testing?
Testing finds bugs. QA ensures the process consistently delivers quality outcomes across teams and releases.
3. Which testing catches most bugs early?
Unit and integration testing capture 60–70 % of defects before staging.
4. What causes flaky automated tests?
Unstable environments, dynamic selectors, or rigid waits. Fixing waits and data determinism reduces flakes.
5. When should manual testing still be used?
For exploratory, usability, and visual scenarios where human intuition beats automation.

Stephen Sweeney, CEO of of Uprite.com, with 20+ years of experience brings tech and creativity together to make cybersecurity simple and IT support seamless. He’s on a mission to help businesses stay secure and ahead of the game!